This post answers the question "How does molecular beam epitaxy work?". Molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) is the technique of semiconductor material growth - a…
Category: Learning
Nanoelectronics: Semiconductors manufacturing
In accordance with recent marketing research by Technavio, published on the Business Wire website in 2017, the top five leading global semiconductor foundry players…
Rectangular waveguide
This post answers the question "What is rectangular waveguide?". In order to find the transmission line impedance and the fields in the transmission line,…
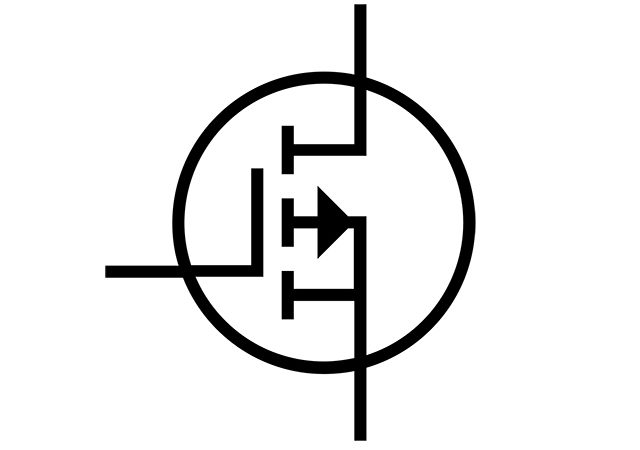
Depletion MOSFET
A depletion MOSFET is a one state transistor, that is in an ON state even when the gate to source voltage VGS or VGSS…
Circular transmission lines
A circular waveguide is schematically depicted in Figure 5. To consider its parameters we will employ the polar coordinates with radial components ρ and…
Coaxial transmission line
A schematic coaxial transmission line is depicted below and widely used both commercially and industrially, especially in connectors. To obtain the field solution for…
The transmission line as parallel planes, stripes and microstripes
Parallel planes or stripes is the most general example of transmission line. Schematically it is depicted below. The parallel stripes can carry TEM, TM…
Equivalent currents and voltages in network analysis
RF and microwave circuits that operate on small frequencies can be treated like circuits with lumped parameter components. If the components are small enough,…
L-section impedance matching
The matching impedance process for RF circuits is very important. Impedance matching is also called the tuning process. Physically it represents the circuit between…
Single-stub and double-stub matching
Stub tuning is an impedance matching technique, when an open-circuited or short-circuited transmission line is connected to the main transmission line. A stub is…