In this post we calculate the total power dissipation in CMOS inverter. The total power of an inverter is combined of static power and dynamic power.
Let’s consider the inverter representation depicted on the figure below, and let’s imagine that there is a square alternating wave on the input of the inverter.
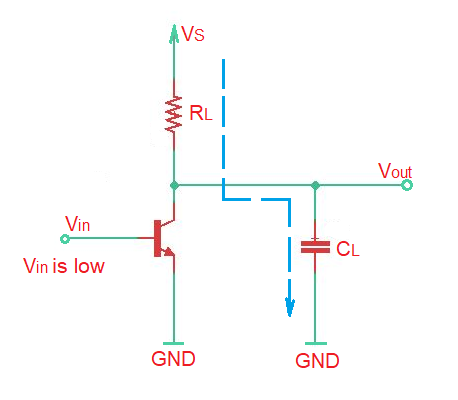
When the voltage of the square wave is low, the MOSFET is OFF. The load capacitor is charged up to the voltage via the load resistor .
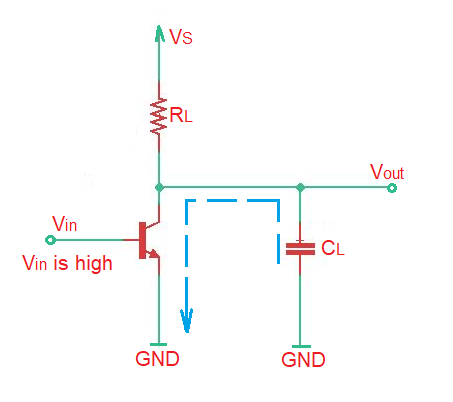
When the MOSFET is ON, the load capacitor discharges through the MOSFET resistance, and finally the capacitor voltage will reach the voltage level . (figure below)
The total power dissipated on the inverter can be found as .
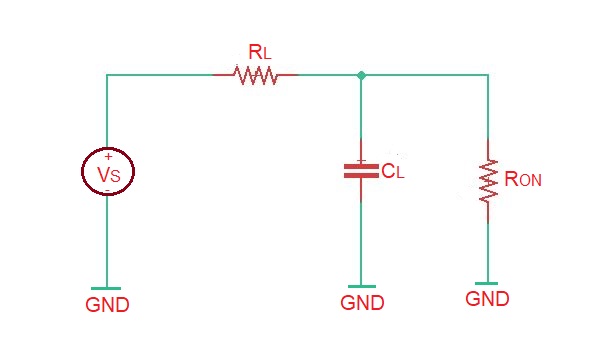
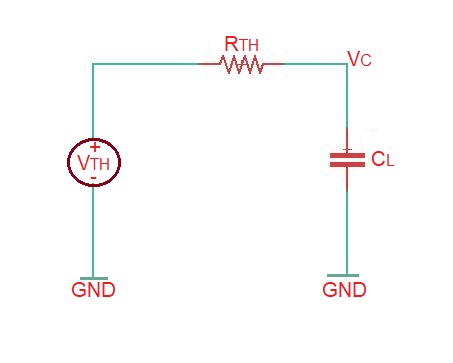
- Let’s calculate what energy will dissipate during interval of time when the signal is high. In this case we can get the equivalent circuit depicted below, and in addition we can also transform this circuit in accordance to Thenevin theorem.
Similarly to calculations made before, we can find the nodal voltage as the solution of the differential equation, and the the result , . Knowing that at the moment capacitor voltage was , when the capacitor charges till voltage . So we can get the expression for the energy
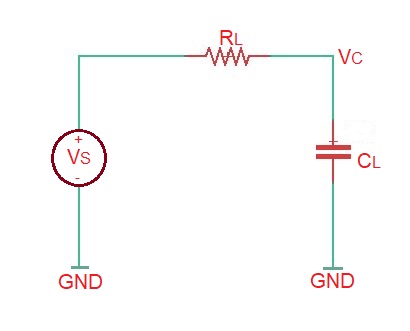
2. Now let’s calculate the energy dissipated during the interval when the inverter signal is low. In this case the equivalent circuit looks as below:
And the nodal voltage can be found as . Here when the the , and when the . Then dissipating energy for the period of time is .
Then the total dissipated energy is , then the total power dissipation of the CMOS inverter is . Referring to the beginning of the discussion that the dissipated power consist of static and dynamic power, we can conclude that and dynamic power , where .
Educational content can also be reached via Reddit community r/ElectronicsEasy.