This post answers the question “What is the difference between NAND and NOR flash memory?”. Nonvolatile memory is a memory that keeps it content even not powered. Nonvolatile memory can be in different forms.
ROM – read only memory, data written once, allows multiple read access.
PROM – programmable read only memory, data written once (not at the manufacture process, but anytime later), allows multiple read access.
EPROM – erasable programmable read only memory, it can be reprogrammed after erasing the content by ultraviolet light exposure.
EEPROM – electrically erasable programmable read only memory, can be erased with voltage pulses. It can be rewritten limited amount of times. Ant it stores data for a limited time only.
Flash EEPROM – more advanced than EEPROM and fast. Allows to erase and store data in blocks, but not in bytes.
Flash memory is currently very popular. Two the most popular types are: NOR and NAND flash memory.
NOR and NAND flash memory are different by their architecture and purpose.
NOR memory is used for storing code and execution. Allows quick random access to any location in memory array.
NAND memory is used for data storage . Requires relatively long random access. Programming and erasing is easier than in NAND memory. Cost of bit of NAND memory is cheaper that NOR memory.
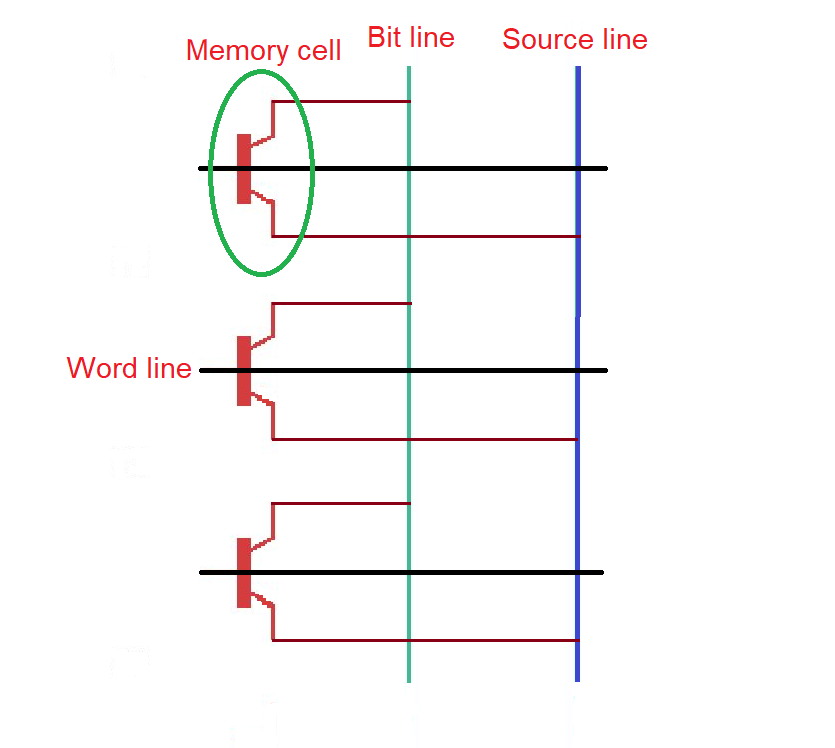
Flash memory architecture based on floating gate technology. In NOR flash memory every memory cell is connected to the floating gate. In NAND flash memory, several memory cells are connected in parallel. (depicted below).
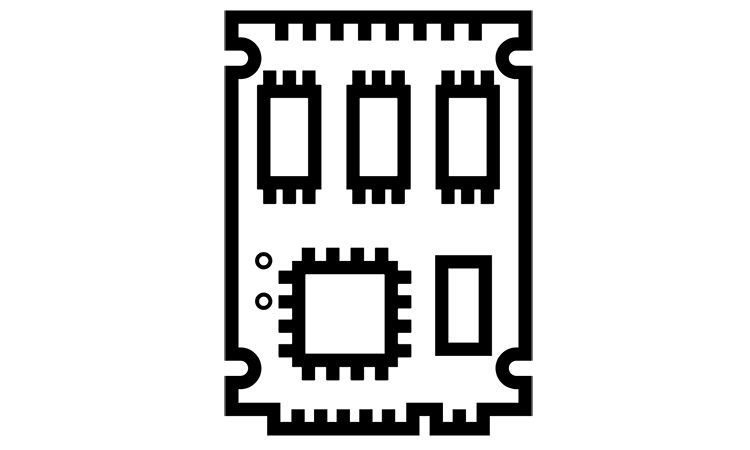
NOR flash architecture.
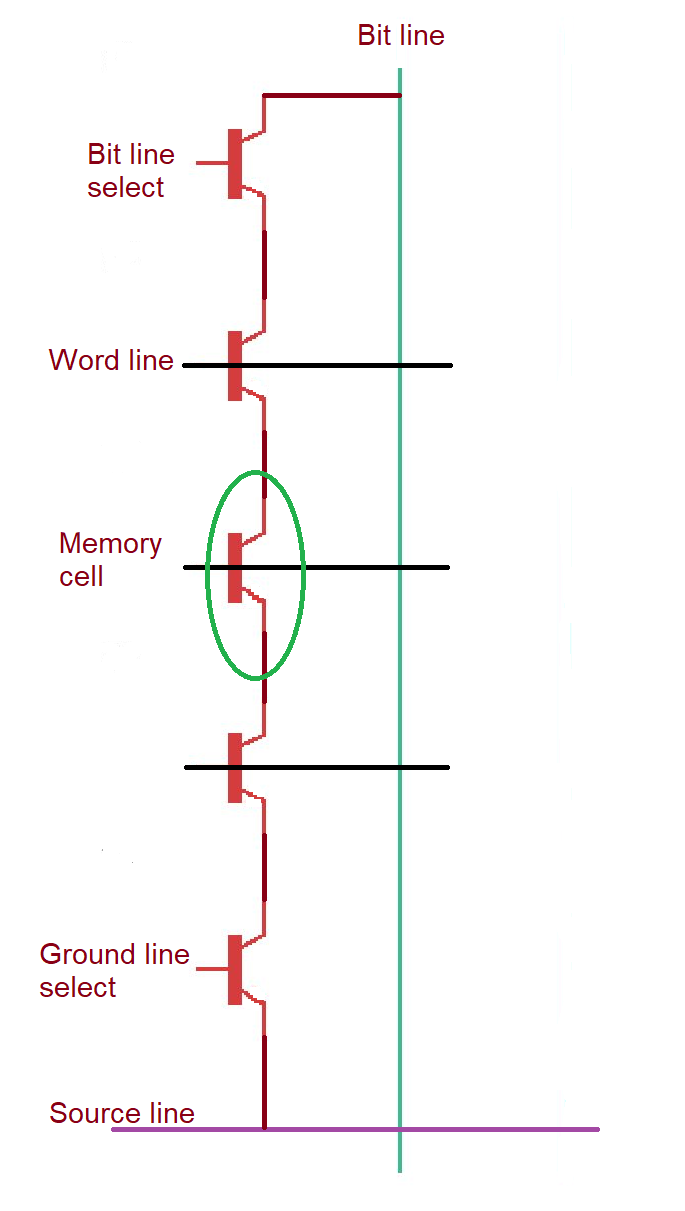
NAND flash architecture.
NOR flash memory gives enough address lines to map all memory range. It gives fast random access and short read time. The disadvantage is low programming and erasing speed, and as soon as NOR memory cell is big enough, it makes it expensive.
NAN memory cell is smaller and cost less, has higher program/erase speed. However it has low read speed and does not allow random access. Code execution is different and a bit more complicated with NAND memory that NOR memory.
Density of NAND memory is much higher than density of NOR flash memory. NAND flash memory density is now until 512Gb available, at the same time NOR flash memory is only up to 2Gb.
NAND and NOR flash memory structure is based on erase blocks. Smaller the block size – faster erase speed. However smaller blocks are, the bigger amount of them is needed and bigger the die size of the flash memory.
NAND memory is usually read with pages (inside the block structure) to reduce the read time. The content of the page is read sequentially with address and command cycles.
Both flash memory devices should be erased before reprogramming.
Accessing NAND memory devices is more complicated, requiring a sequence of commands on the 8-bit bus. Data of the NAND memory is accessed in pages, as mentioned above, around 528bytes length. NAND memory is unsuitable for booting, but great as a hard drive disk.
NAND flash devices do not have any movable parts, they are solid-state devices, comparing to magnetic hard disc. It makes them perfect for embedded applications.
More educational content can be accessed via Reddit community r/ElectronicsEasy.
Sources:
“Embedded hardware: Know it all”
“Flash 101: NAND flash vs NOR flash”, embedded.com