Group of researches from University of Pennsylvania and Purdue University have made a study of Emojis usage around the world. Two categories of people were chosen for conducting a study – western culture (United States of America and Canada), and eastern culture (Japan and China). In order to conduct this laborious process machine learning metjods were highly in use.
Researchers were interested to get answers to several questions, including how frequently different categories of people use certain emojis and how distinctive emojis across cultures. In order to study human Emoji habits, researches were exploring two platforms – Twitter and Weibo. Emojis are symbols standardised at The Unicode Standard 11.0, including smileys, objects and another symbols.
This work was approved by he University of Pennsylvania’s Institutional Review Board. Tweets and Weibo messages were filtered by language – Tweets written by any language different from English in the UK, USA and Canada, Japanese in Japan, and chineese in China were removed from the study.
All left messages and tweets were tokenized. Key differences were measured using LIWC dictionaries. Preparational stage was arranging all tokens into vectors using Word2Vec stage using Gram-Schmidt algorithm. Next step was calculating cosine similarities across countries. And at the end – calculation of Spearman correlation coefficients.
As a result, among used 1281 Emojis, 602 Emojis appeared in the results, and 528 appeared more than 1000 times. Researchers noticed the lowest similarity in usage of symbols related to Food and drinks and activities. This tells about distinctive differences between cultures. The results also revealed similarity of correspondence between LIWC categories and Emojis. The most similar categories are Anger, Money, Family, Food and some others. However there is also some differences as well, related to categories of Friendship, Work, Time and some others.
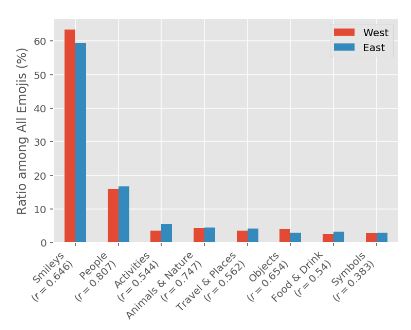 Frequency of Emojis, grouped by categories.
Frequency of Emojis, grouped by categories.
Source: Proceedings of the Thirteenth International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media (ICWSM 2019), Sharath Chandra Guntuku, Mingyang Li, Louis Tay, Lyle H. Ungar, University of Pennsylvania, Purdue University.”Studying cultural differences in Emoji usage across the East and West”
This research work outlined very wide analysis of Emoji usage based on frequency, context, and topic associations across western and eastern cultures, using ML computational methods.
Here you can read the research work in detail.
Credit: “Studying cultural differences in Emoji usage across the East and West”, Proceedings of the Thirteenth International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media (ICWSM 2019), Sharath Chandra Guntuku, Mingyang Li, Louis Tay, Lyle H. Ungar, University of Pennsylvania, Purdue University.”Studying cultural differences in Emoji usage across the East and West”




