As technological innovations continue to spring up and reshape industries, additive manufacturing has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionising the way we design, create, build, and think when it comes to manufacturing.
Commonly known as 3D printing, the additive manufacturing process involves the layer-by-layer assembly of materials to produce three-dimensional objects from digital models. While the process might seem like a concept from science fiction, which it once was, its practical applications are now rapidly transforming various sectors ranging from aerospace, healthcare, construction, automotive, and beyond.
Where are we seeing additive manufacturing take hold?
The ground-breaking technology has found its way into numerous industries, challenging traditional manufacturing methods with its flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. One of the major advantages of the approach lies in its ability to create complex designs and intricate geometries that are either a significant challenge or unattainable through traditional means. This flexibility has significantly impacted industries like aerospace and automotive, where lightweight, intricately designed components are crucial for enhancing performance and fuel efficiency.
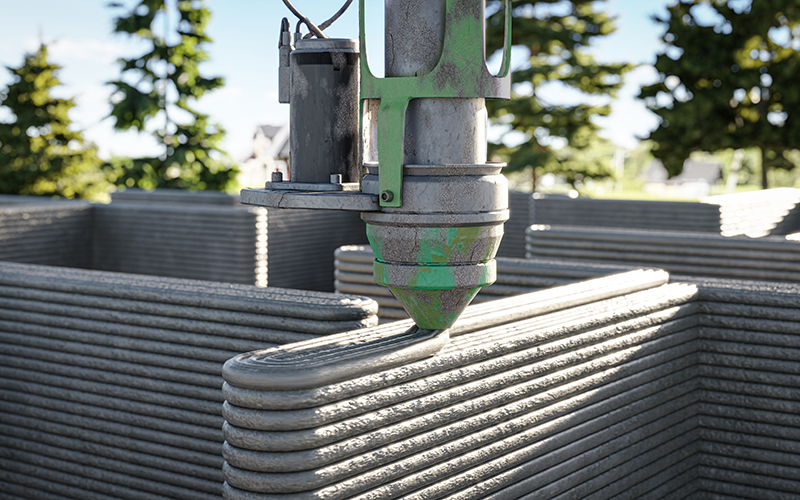
Within architecture and construction additive manufacturing has continued to gain significant traction enabling the construction of complex structures with unprecedented design freedom. With the ability to use various materials, including concrete, plastics, and metals, architects and construction engineers can explore innovative designs and sustainable building practices, reshaping the future of urban landscapes. It will also enable a more cost-effective, efficient method of creating housing at mass in areas which need it most, and the technology will only continue to advance with time.
Within the medical field, additive manufacturing has revolutionised the production of customised implants, prosthetics, and even bio-printed tissues, offering tailored solutions that cater to the unique needs of patients. By leveraging advanced materials and precise modelling techniques, medical professionals can now provide patients with personalised, life-changing treatments that were once considered unimaginable.
Furthermore, additive manufacturing has transformed the landscape of traditional factories by optimising production processes, reducing lead times, and enabling on-demand manufacturing. The technology has streamlined the production of complex components and customised parts, eliminating the need for specialised tooling, and reducing overall production costs. This has allowed factories to shift towards a more flexible and agile manufacturing approach, where customisation and small-scale production runs are feasible without incurring substantial setup costs. The technology, being almost entirely automated in design can also mean that manufacturing processes of intricate products can be completed un-manned or overnight, massively improving throughput.
Moreover, additive manufacturing has facilitated the rapid prototyping of products, allowing manufacturers to test and iterate designs more efficiently before mass production. This iterative process has significantly accelerated product development cycles and enabled manufacturers to bring products to market faster, gaining a competitive edge in dynamic industries.
Additive manufacturing in future careers
Additive manufacturing, like many of the other emerging technologies out there, is ripe with potential career prospects for young engineers, especially as it only continues to expand.
From materials engineers specializing in the development of innovative printing materials to design engineers proficient in creating intricate digital models, the field offers a diverse range of roles. Additive manufacturing also necessitates skilled technicians capable of operating and maintaining 3D printers, as well as quality control specialists ensuring the integrity and precision of the printed products. As the technology continues to advance, there is an increasing demand for research and development professionals dedicated to pushing the boundaries of additive manufacturing and unlocking its full potential across various industries.
Some potential job vacancies in additive manufacturing may include additive manufacturing design specialists, materials scientists/engineers, process engineers, technicians, quality assurance, or research and development.
Concluding thoughts
Additive manufacturing stands as a testament to the endless possibilities that arise when technology meets innovation. Its ability to redefine manufacturing processes, accelerate product development, and foster unparalleled creativity underscores its vital role in shaping the future of diverse industries. As this technology continues to evolve and expand its reach, the opportunities for both professionals and industries alike are boundless, paving the way for a future where the only limit is one’s imagination.