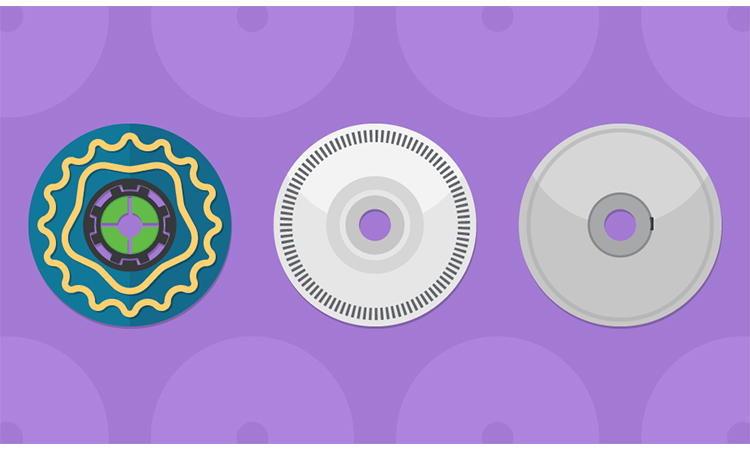
Used across a multitude of industrial settings, rotary encoders are crucial to reliable and accurate motion control in applications such as industrial process control, robotics and automation equipment. Susceptible to the many hazards present, there are advantages and trade-offs between the three main encoder technologies.
Optical encoders might have dominated the motion control sector for decades, but they are particularly vulnerable to oil, dust and dirt, a build-up of which can conceal code wheel markings. In addition, as well as high current consumption, an optical encoder’s lifespan can be limited by the duration of its LED. On the other hand, magnetic encoders might be more robust when it comes to contaminants like moisture, dirt and oil, but they offer lower resolution and accuracy, and operate within a limited temperature range. Capacitive encoders, however, provide a useful alternative that delivers the benefits of both optical and magnetic types to offer further advantages including greater durability, smaller footprints and lower current consumption.
This CUI Devices blog, titled “Capacitive, Magnetic, and Optical Encoders – Comparing the Technologies”, considers the technologies of the three main encoder types, assessing their key benefits as well as the trade-offs of each.