The previous module showed the characteristics of semiconductors and their variety under different conditions. Here we will briefly recap the main characteristics of semiconductors…
Category: Year 1
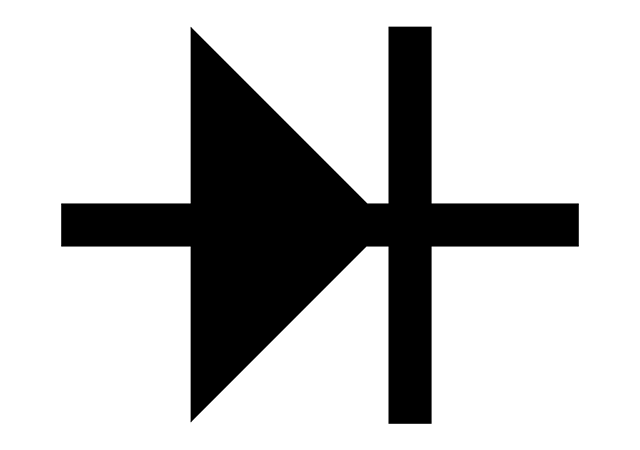
P-N junction in semiconductors
This post is covers the topic of pn junction definition. A semiconductor itself does not give any special properties to a semiconductor device. However,…
Large signal diode models
Ideal diode model: describes the diode as an on-off device. The ideal diode can be approximated to the open-circuit and short-circuit device. In the…
Small-signal diode models
The idea of small-signal modelling is that the short-cut part of the current-voltage characteristic of the semiconductor diode is not precise enough in an…
Signal processing diode applications
Limiter A limiter is a diode circuit that is designed to keep voltages at the load in a certain voltage range –Vmin<VL<Vmax, so the…
Transistor as an amplifier
A transistor is a three-terminal semiconductor device that can perform amplification and switching functions. The operation of a transistor as a linear amplifier is…
What are MOS devices
A MOS-device is a simplified example of a MOSFET structure (without source and drain). Let's consider how the MOS-device works. The simplest MOS-device has…
Coulomb’s law. Electric field.
Electric charge is a measure of the elementary particles that enable electrical and magnetic interactions. Electric charge, is the basis for Coulomb Law, and…
Divergence theorem
The Coulomb Law and superposition principle can lead to divergence theorem which is valid for bilateral, axial and spherical charged objects. Let’s divide the…
Electrostatic field and potential difference
We know how to find the potential difference between two points in the electrostatic field: φ1-φ2=∫12Eldl Let’s find out the reverse dependence - electrostatic…